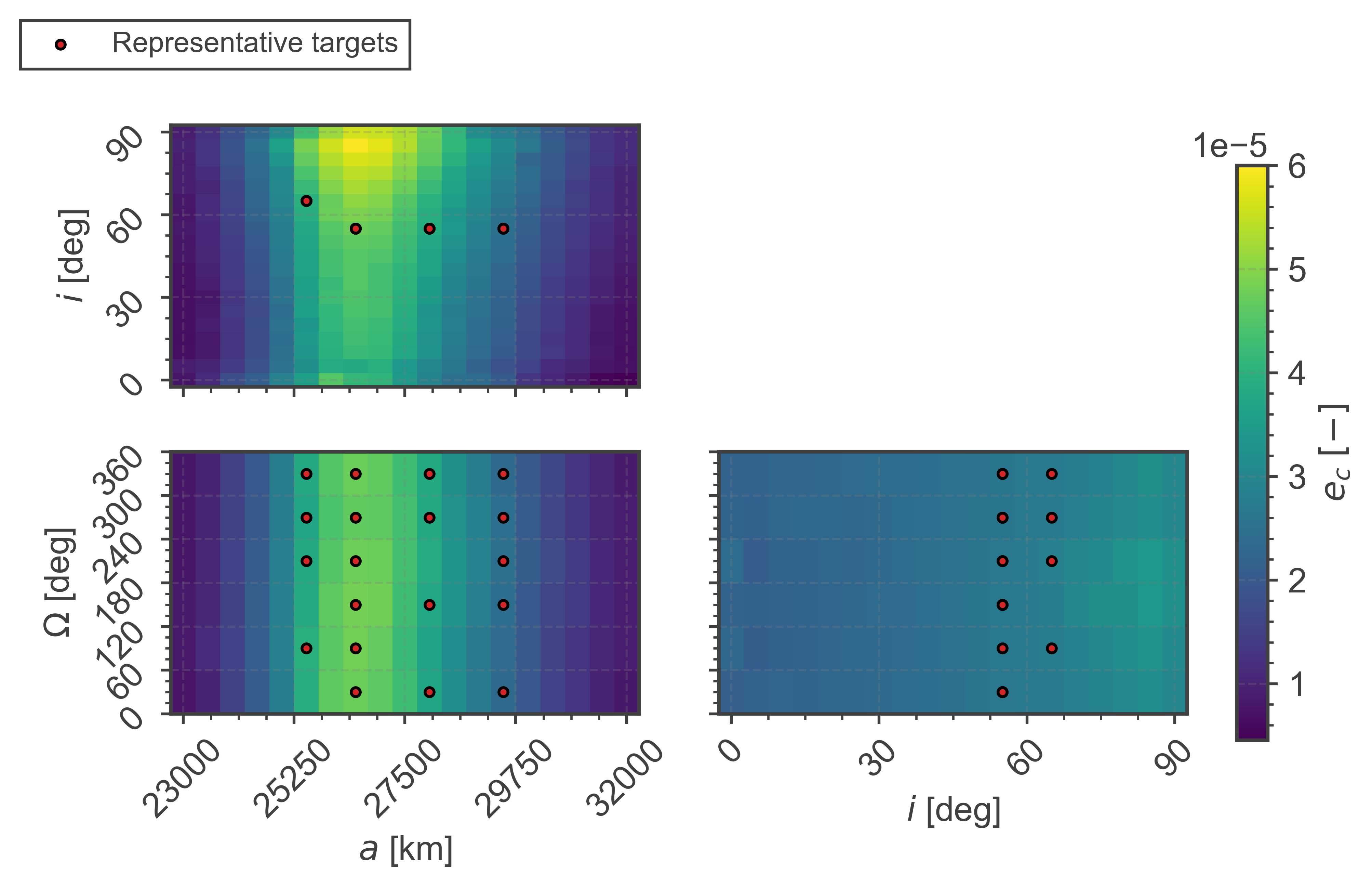
Ranking space missions based on their likelihood to contribute to the proliferation of space debris is crucial to foster a sustainable use of space. The new paper published by Lorenzo Giudici, Juan Luis Gonzalo, Andrea Muciaccia and Camilla Colombo from Politecnico di Milano, and by Francesca Letizia from the European Space Agency presents the extension of the space debris index formulation ECOB (Environmental Consequences of Orbital Breakups) to the medium Earth orbital region. The currently in-orbit missions are eventually ranked based on the proposed metric.
The metric has been formulated for the THEMIS (Track the Health of the Environment and Missions in Space) software, in an ESA-funded project carried out by Politecnico di Milano in collaboration with DEIMOS UK.
The paper is available here.